Copyright © 2004 Cascade BioScience, Inc. All rights reserved.
| Description | Catalog # | Vial Size | Price (USD) |
| Anti-Murine CD36 (clone 63) | ABM-5525 | 100 ug | $295 |
|
|
|
|
Immunoprecipitation:
|
1:1000 dilution |
|
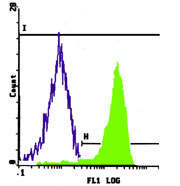
Flow Cytometry
|
1:1000 dilution |
|
Immunofluorescence:
|
1:1000 dilution |
|
Funtional Studies
|
recommended |
|
Reactivity:
|
rat, mouse; others likely |
|
|
|
|
Immunogen:
|
full-length adenovirus vector injected into CD36 null mice |
|
Host/Ig Type:
|
mouse monoclonal IgA |
|
Purification:
|
protein L chromatography |
|
Quality Control:
|
Flow Cytometry using elicited mouse peritoneal macrophages incubated with CD36 antibody |
|
|
|
|
Storage:
|
-20˚C |
|
Stability:
|
1 year |
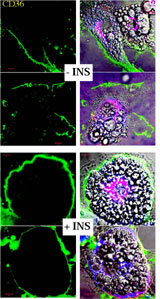
Dawson, D.W., Pearce, S.F.A., Zhong R., Silverstein, R.L., Frazier,W.A., and N.P. Bouck. (1997) "CD36 Mediates the Inhibitory Effects of Thrombospondin-1 on Endothelial Cells." J. Cell Biology 138: 707-717
Febbraio, M., Abumrad, N.A., Hajjar, D.P., Sharma, K., Cheng W., Pearce, S.F.A., and R.L. Silverstein. (1999) "A null mutation in murine CD36 reveals an inportant role in fatty acid and lipoprotein metabolism." J. Biol. Chem 274:19055-19062
Silverstein, R. L. and M. Febbraio. (2000) "CD36 and Atherosclerosis. Current Opinions in Lipidology." 11:483-491
Chien-Ping Liang, Seongah Han, Haruka Okamoto, Ronald Carnemolla, Ira Tabas, Domenico Accili, and Alan R. Tall “Increased CD36 protein as a response to defective insulin signaling in macrophages” J Clin Invest. 2004 March 1; 113 (5): 764–773
full text
Lynn Corcoran, David Vremec, Maria Febbraio, Tracey Baldwin and Emanuela Handman “Differential regulation of CD36 expression in antigen-presenting cells: Oct-2 dependence in B lymphocytes but not dendritic cells or macrophages” International Immunology, Vol. 14, No. 10, pp. 1099-1104, October 2002
full text
Kuniyasu A, Ohgami N, Hayashi S, Miyazaki A, Horiuchi S, Nakayama H.”CD36-mediated endocytic uptake of advanced glycation end products (AGE) in mouse 3T3-L1 and human subcutaneous adipocytes.” FEBS Lett. 2003 Feb 27;537(1-3):85-90.
Abstract 6 more...